Gartner analysts Ali Merji, Gladys Yeo and Leeann Ji recently published a report: ‘How Asia/Pacific Banks Responded to COVID19 and What CIOs Can Learn’. Here are some highlights and examples from the report:
 Analysis of how Asia-Pacific banks responded to the covid19 outbreak has yielded 4 key imperatives. BFSI CIOs have had to take on new responsibilities and make quick decisions related to preserving the business, meeting highly emotional customer needs, keeping clients and employees safe, and supporting employees in new ways of working. Many banking leaders continue to navigate through this unfamiliar environment and look to Asia-Pacific as a source of learning, because the region was exposed to covid impacts much earlier than the rest of the world. This research explores how banks and investment firms in Asia-///Pacific have responded to the pandemic, and derives lessons learned for banking leaders around the world to use as a guide to formulate their own strategies.
Analysis of how Asia-Pacific banks responded to the covid19 outbreak has yielded 4 key imperatives. BFSI CIOs have had to take on new responsibilities and make quick decisions related to preserving the business, meeting highly emotional customer needs, keeping clients and employees safe, and supporting employees in new ways of working. Many banking leaders continue to navigate through this unfamiliar environment and look to Asia-Pacific as a source of learning, because the region was exposed to covid impacts much earlier than the rest of the world. This research explores how banks and investment firms in Asia-///Pacific have responded to the pandemic, and derives lessons learned for banking leaders around the world to use as a guide to formulate their own strategies.
BFSI CIOs must now proactively think about emerging market needs as the situation progresses and about the financial and economic impacts that will follow. For example, DBS Bank is engaging with startups Oddle and FirstCom Solutions to provide food and beverage establishments with the ability to set up an online presence in just 3 business days. This will help food and beverage businesses, especially those new to e-commerce, to quickly amplify social media marketing and offer delivery service to sustain revenue during the crisis.
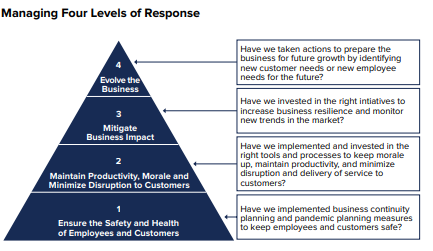
Gartner recommends 4 best practices for CIOs, as shown in the diagram.
Practice No. 1: Ensure Safety & Health of Employees & Customers
Banks and other financial services firms implemented measures to ensure essential physical channels were available to support the immediate needs of customers. Banks also took on the role of educator and information provider by instructing customers to wear face masks and observe social distancing. Following the SARS outbreak in 2003, some banks in Hong Kong and Singapore had developed and practiced pandemic scenarios in their BCPs that included remote and split-site working arrangements.
To counter covid, the Postal Savings Bank of China implemented pandemic control measures in its branches across the country. These requirements included having both staff and customers use face masks, disinfecting the branch 4 times a day, rotating service staff to ensure continued in-person interactions, and frequently taking the temperatures of staff and customers.
Shinhan Bank and most other Asia-Pacific-based banks post covid updates on their websites that instruct customers to use drive-throughs and social distancing measures if they need to come to the bank.
HSBC Hong Kong published an article highlighting the efforts of 2 employees who regularly checked in on their branch colleagues and even invited a psychologist to host an online counselling session for them. The bank also shared messages of gratitude to unsung heroes on its tower and dedicated it to those who ‘care for us, keep us going and give us hope.’
Practice No. 2: Maintain Productivity & Morale; Minimize Disruption to Customers
CIOs should maintain transparency about service delays and proactively reach out to customers to inform them about relief programs. CIOs must also remove barriers to accessing help and enable customers to confidently switch to online self-service channels.
For example, Westpac uses Twitter to update its customers on processing or call center delays due to significant demand for its financial support packages. The bank’s website also has a continually updated banner notifying customers of high call volumes and linking them to resource pages based on their needs. To alleviate pressure on certain channels, Westpac uses Twitter to encourage customers to use online and mobile banking channels to help wherever possible.
Mizuho Bank launched a proof-of-concept trial of its digital ID service, which uses facial biometrics and device location information for online authentication and ongoing customer due diligence.
As a majority of ANZ’s employees transitioned to working from home, the bank’s CEO encouraged headquarters office staff to avoid using certain systems. This freed up limited bandwidth for frontline employees to respond quickly to customer needs and requests. As a result, ANZ’s covid customer hub was launched on the website within 72 hours.
Standard Chartered in Hong Kong is promoting its new My RM tool as a way for customers to invest and interact with relationship managers through digital channels. The My RM function is embedded into Standard Chartered’s online and mobile banking platforms, and it enables private banking clients to speak with their relationship managers through texts and audio calls, live share files and documents, and access market trends.
Krungsri (Bank of Ayudhya) through its consumer loan unit publicly announced its commitment to prioritize financial assistance over business growth, predicting that the business will contract for a full year. As part of its debt-restructuring plan, Krungsri’s consumer loan unit automatically applied its debt moratorium to all customers and lowered interest rates for personal loans, with the condition that customers use the bank’s mobile app to apply.
Tencent, through its insurance arm WeSure, launched a covid medical worker insurance plan on January 29 with AXA and DingXiangYuan in China, which pays cash compensation upon diagnosis. Over 100,000 medical professionals across China signed up for the plan within just one week of its rollout.
Practice No. 3: Mitigate Covid19’s Business Impact
CIOs must improve real-time listening to detect shifts in customer sentiment. As sentiments and behaviors change, banks should focus their data analytics capabilities on monitoring consumer trends. CIOs should align data analytics investments with current and future business goals to encourage stakeholder support. CIOs can then use the insights to prioritize initiatives when cost optimization and investment decisions are to be made.
For example, Hang Seng Bank in China opened branches in February 2020, but few customers came to conduct transactions in person. Instead, customers exponentially increased their use of Hang Seng Bank’s mobile, online, telebanking and electronic banking services. As a result, the bank committed to promoting and launching more digital banking capabilities in the retail banking and wealth management business lines so that customers don’t have to come into the branch. This also prepares the bank for any future pandemic waves (or other crises) and accelerates the transition to a higher percentage of digital interactions.
Standard Chartered clients are using bank data to drive analytics and create realtime dashboards, creating innovative solutions to enhance its clients’ experience.
Alibaba Group created flexible job openings and an employee-sharing scheme among its affiliates, in addition to providing merchants interest-free loans via its banking arm MYbank. It also provides businesses access to various resources in the Alibaba ecosystem free of charge, including Taobao Live services for all offline merchants, online courses from Taobao University and proprietary services from its logistics provider Cainiao.
Practice No. 4: Evolve the Business Model
Covid could result in new customer behaviors and attitudes in the near future. Firms must identify these new customer behaviors as they occur, as well as the extent to which the behaviors are entrenched within each local market. In addition, banks should expand their footprint in less profitable segments by connecting customers to government relief programs. This mitigates risks for the bank, while serving the needs of customers.
For example, ICICI Bank in India developed a suite of digital banking services and APIs that enable customers to access over 500 banking services on the bank’s app or website. The ICICI stack includes online account opening, which noncustomers can use to access the bank’s virtual services. The bank is using this opportunity to push higher usage of its API stack to expand its footprint.
United Overseas Bank (UOB) is offering its digital platform, UOB BizSmart, at lower prices to its customers. UOB BizSmart provides a suite of integrated services that enable businesses to remotely manage multiple core processes, such as sales, invoicing, payroll and accounting.
Bank of Jilin in China created a wealth management product for pandemic control. The product invests clients’ assets into epidemic prevention assets.
Indian Bank launched 3 new products to support farmers, poultry producers and workers in the informal employment sector during the current crisis, using various government-supported relief programs.
Standard Chartered signed a strategic agreement to introduce the Infor Nexus network to the bank’s clients to ease supply chain friction, while offering suppliers much-needed capital.
BNP Paribas co-created digital tools in collaboration with corporations and fintechs for reconciliation and cash forecasting. One of the tools aggregates payment information from e-wallets into a single reporting format and feeds it into transaction management systems and ERP platforms for seamless reconciliation.







